Countdown Details: Starliner Launch Countdown
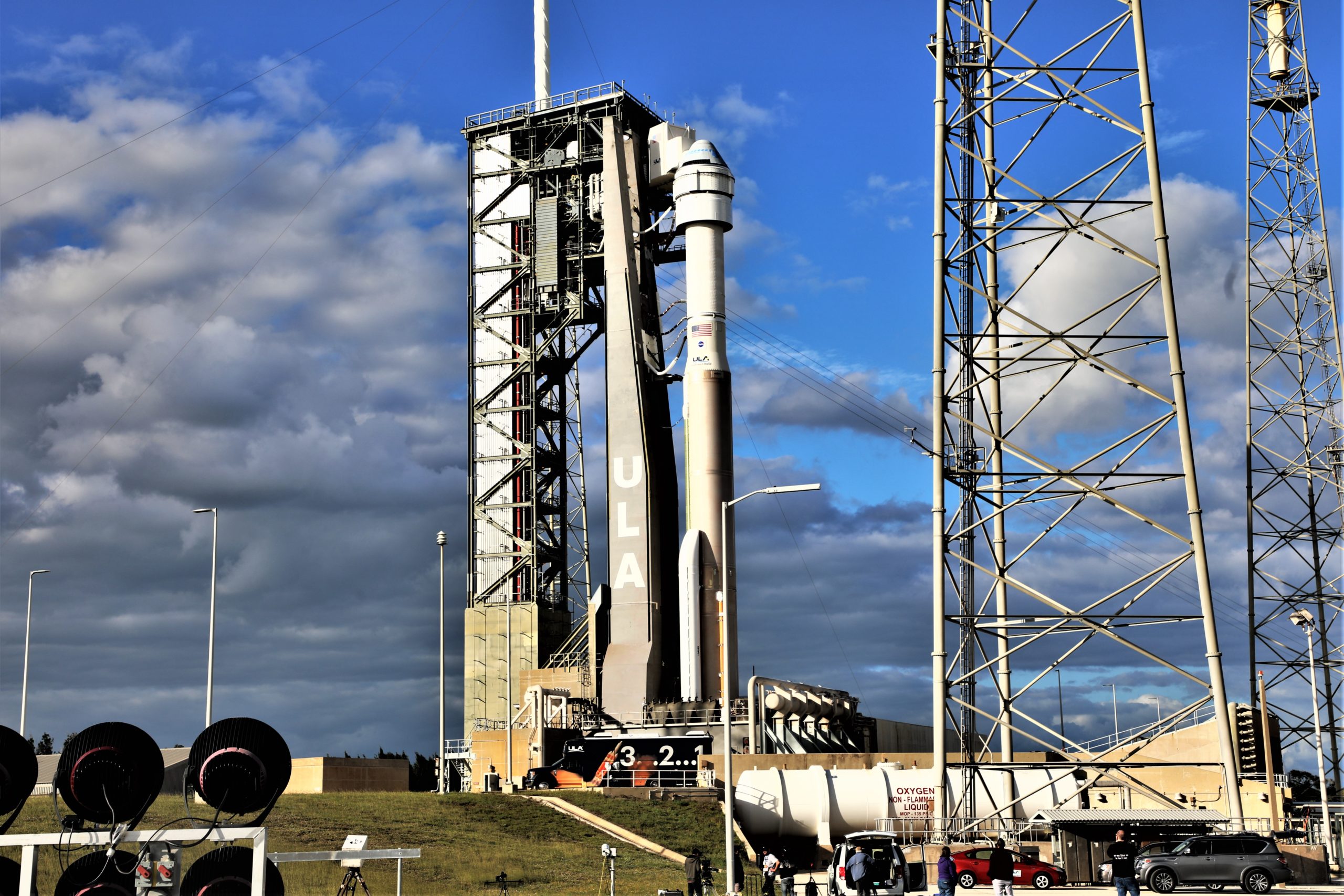

The Starliner launch countdown is a meticulously orchestrated sequence of events leading up to the spacecraft’s liftoff. Each stage of the countdown serves a critical purpose, ensuring the mission’s safety and success.
The Starliner launch countdown is in full swing, with the spacecraft set to lift off from Cape Canaveral in just a few hours. Meanwhile, on the legal front, the poppi soda lawsuit continues to make headlines. The plaintiffs in that case allege that the popular sparkling water contains harmful chemicals that can cause a range of health problems.
While the company denies these claims, the lawsuit has cast a shadow over the brand’s reputation. Back to the Starliner launch, NASA is confident that the spacecraft is ready for its mission to the International Space Station. The launch is scheduled for 6:55 AM EST, and you can watch it live on NASA TV.
The countdown typically begins several hours before the scheduled launch time. During this period, engineers conduct final checks on the spacecraft and launch vehicle, verify all systems are operational, and load the flight software.
As the countdown to the Starliner launch intensifies, the anticipation builds for Boeing’s pivotal mission today. This launch, closely watched by the industry, will mark a significant milestone in the company’s commercial space ambitions. As the Starliner prepares for its journey, we turn our attention to Boeing’s launch today , an event that promises to propel the Starliner launch countdown even further into the realm of possibility.
Pre-Launch Checks, Starliner launch countdown
- Powering up the spacecraft and launch vehicle
- Verifying communication systems
- Checking fuel levels and pressurization
- Loading flight software
Terminal Countdown
The terminal countdown commences approximately 10 minutes before launch. During this phase, the launch vehicle is fueled, and the spacecraft is pressurized and armed. The crew, if present, boards the spacecraft and prepares for liftoff.
- Fueling the launch vehicle
- Pressurizing the spacecraft
- Arming the spacecraft systems
- Crew boarding (if applicable)
Final Countdown
The final countdown begins at T-9 minutes. During this critical phase, the launch vehicle’s engines are ignited, and the spacecraft is released from the launch pad. The spacecraft then ascends through the atmosphere, powered by the launch vehicle’s engines.
- Engine ignition
- Spacecraft release
- Ascent through the atmosphere
Mission Success
Upon reaching orbit, the spacecraft separates from the launch vehicle and begins its mission. The launch countdown culminates in the successful deployment of the spacecraft into its intended orbit, marking the beginning of its mission objectives.
Mission Objectives
The Starliner mission embarks on a multifaceted endeavor, encompassing both primary and secondary objectives that will significantly contribute to the advancement of space exploration.
The mission’s primary objective centers on demonstrating the spacecraft’s capabilities for transporting crew and cargo to and from the International Space Station (ISS). This entails conducting a successful launch, rendezvous, docking, and return to Earth, showcasing the Starliner’s reliability and safety as a viable means of human spaceflight.
Furthermore, the mission aims to accomplish a range of secondary objectives, including conducting scientific experiments, testing new technologies, and gathering valuable data on human health and performance in space. These objectives are crucial for advancing our understanding of the effects of long-duration spaceflight on the human body, paving the way for future deep space exploration missions.
Scientific Advancements
The Starliner mission carries a suite of scientific experiments designed to explore various aspects of space science and human biology. These experiments will delve into topics such as:
– The effects of microgravity on plant growth and development
– The impact of space radiation on human cells
– The development of new materials and technologies for space exploration
The findings from these experiments will provide valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities associated with long-duration spaceflight, enabling scientists to develop strategies for mitigating the risks and maximizing the benefits of future missions.
Technological Advancements
The Starliner mission serves as a testbed for a range of cutting-edge technologies that are essential for future space exploration endeavors. These technologies include:
– An advanced guidance, navigation, and control system
– A new docking system
– A life support system designed for long-duration missions
The successful demonstration of these technologies will pave the way for the development of more capable and efficient spacecraft, enabling humans to venture farther into space and explore new frontiers.
Potential Impact
The Starliner mission is not merely a technological demonstration; it is a stepping stone towards a future where humans routinely travel to and from space. The mission’s success will:
– Boost confidence in the safety and reliability of commercial spacecraft
– Reduce the cost of space transportation
– Expand the possibilities for scientific research and exploration
Ultimately, the Starliner mission is a testament to human ingenuity and our unwavering pursuit of knowledge and discovery. Its success will inspire generations to come and contribute to the advancement of humanity’s presence in space.
Technical Considerations
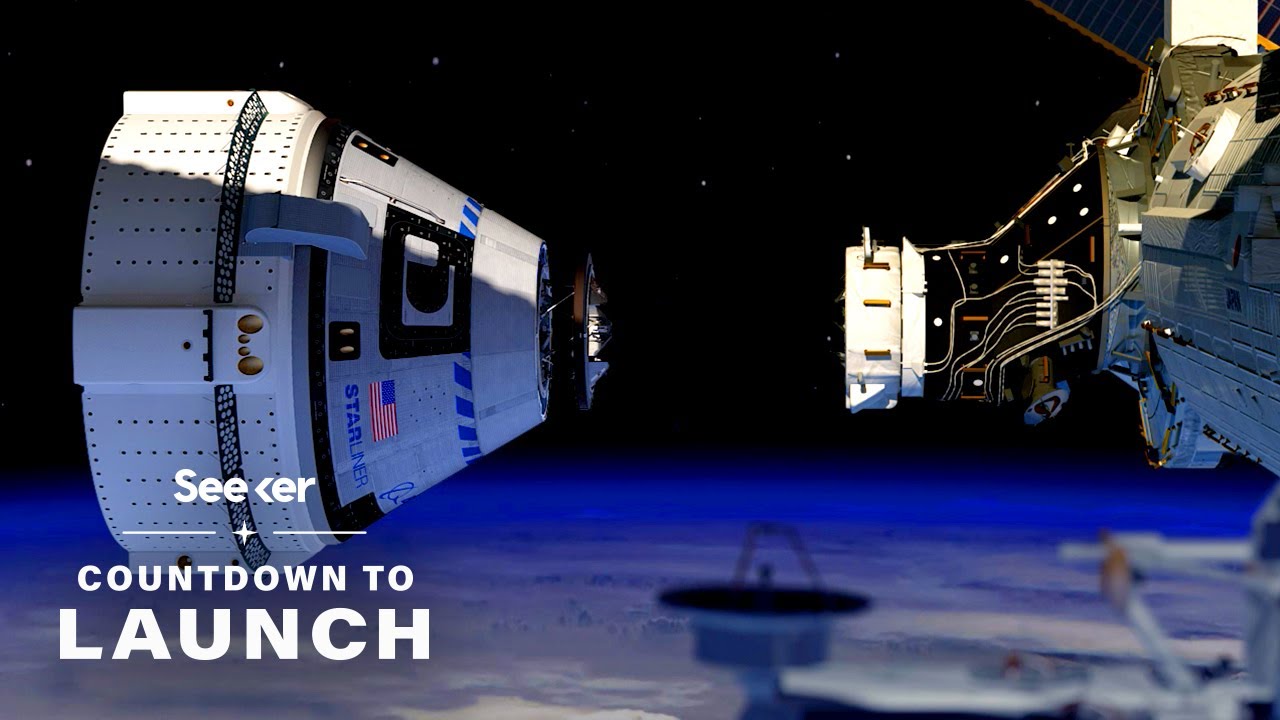
The Starliner spacecraft is a reusable, crew-capable spacecraft developed by Boeing for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. It is designed to transport astronauts to and from the International Space Station (ISS) and other low-Earth orbit (LEO) destinations. The spacecraft consists of a crew module, a service module, and a launch abort system.
The crew module is the habitable portion of the spacecraft, providing a pressurized environment for the astronauts. It is equipped with life support systems, displays and controls, and docking mechanisms. The service module houses the spacecraft’s propulsion systems, power systems, and communications systems. The launch abort system is designed to separate the crew module from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency during launch.
The Starliner is launched on a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket. The Atlas V is a two-stage rocket that uses liquid oxygen and kerosene as propellants. The first stage of the rocket provides the initial thrust for launch, while the second stage places the Starliner into orbit.
Ground control and communication systems play a critical role in the Starliner mission. Ground control is responsible for monitoring the spacecraft’s systems, communicating with the astronauts, and providing guidance and navigation. The communication systems allow the spacecraft to communicate with ground control and other spacecraft in orbit.
Design and Capabilities
The Starliner spacecraft is designed to be reusable, with a lifespan of at least ten missions. It is capable of carrying up to seven astronauts to and from the ISS. The spacecraft is also equipped with a docking system that allows it to attach to the ISS and other spacecraft in orbit.
The Starliner’s service module provides the spacecraft with propulsion, power, and communications. The service module houses four main engines that are used for orbital maneuvers and attitude control. The service module also houses the spacecraft’s solar arrays, which provide electrical power. The communication systems in the service module allow the spacecraft to communicate with ground control and other spacecraft in orbit.
Safety Features
The Starliner spacecraft is equipped with a number of safety features to protect the astronauts in the event of an emergency. These features include:
* A launch abort system that can separate the crew module from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency during launch.
* A redundant flight control system that provides backup control in the event of a failure of the primary flight control system.
* A life support system that provides the astronauts with a pressurized environment, oxygen, and water.
* A fire suppression system that can extinguish fires in the crew module.
The countdown to the highly anticipated Starliner launch is nearing its end, with the spacecraft poised for liftoff at starliner launch time. The mission, which has faced delays and setbacks, marks a crucial step in NASA’s commercial crew program and will pave the way for future space exploration endeavors.
As the countdown continues, excitement and anticipation build among the scientific community and the general public alike, eager to witness the next chapter in human spaceflight.
The countdown to the Starliner launch continues, but like Amanda Knox , it has faced delays and setbacks. Yet, as with Knox’s eventual exoneration, the Starliner team remains determined to achieve success, counting down the moments until it can finally embark on its mission.
The Starliner launch countdown is underway, and excitement is building. The mission, which has been eagerly anticipated by space enthusiasts, is set to be a major milestone in human spaceflight. While we wait for the launch, it’s worth checking out the latest reviews for the new horror film “Acolyte,” which has received mixed reviews on Rotten Tomatoes.
As we count down to the Starliner launch, let’s not forget the thrill of space exploration and the potential it holds for our future.
